







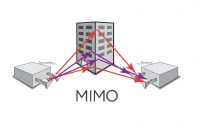
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO (pronounced as "my-moh" or "me-moh"), is a method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmit and receive antennas to exploit multipath propagation.
Early research
MIMO is often traced back to 1970s research papers concerning multi-channel digital transmission systems and interference (crosstalk) between wire pairs in a cable bundle: AR Kaye and DA George (1970),Branderburg and Wyner (1974),and W. van Etten (1975, 1976).Although these are not examples of exploiting multipath propagation to send multiple information streams, some of the mathematical techniques for dealing with mutual interference proved useful to MIMO development. In the mid-1980s Jack Salz at Bell Laboratories took this research a step further, investigating multi-user systems operating over “mutually cross-coupled linear networks with additive noise sources” such as time-division multiplexing and dually-polarized radio systems.
Methods were developed to improve the performance of cellular radio networks and enable more aggressive frequency reuse in the early 1990s. Space-division multiple access (SDMA) uses directional or smart antennas to communicate on the same frequency with users in different locations within range of the same base station. An SDMA system was proposed by Richard Roy and Björn Ottersten, researchers at ArrayComm, in 1991. Their US patent (No. 5515378 issued in 1996) describes a method for increasing capacity using "an array of receiving antennas at the base station" with a "plurality of remote users." Arogyaswami Paulraj and Thomas Kailath proposed an SDMA-based inverse multiplexing technique in 1993. Their US patent (No. 5,345,599 issued in 1994) described a method of broadcasting at high data rates by splitting a high-rate signal "into several low-rate signals" to be transmitted from “spatially separated transmitters” and recovered by the receive antenna array based on differences in “directions-of-arrival.” However, neither patent contemplated the use of co-located antennas at both ends of a radio link in order to exploit multipath propagation.